Measuring blood oxygen levels is crucial to assessing the function of the lungs. Healthcare professionals use blood oxygen levels to detect even the smallest changes in blood oxygenation.
Using a pulse oximeter is an efficient way to get rapid readings, especially when the patient is in critical condition. Depending on the medical specialty, the use of a pulse oximeter can be reserved for emergency settings (e.g., ER doctors) or medical consultations (e.g., pulmonologists). (1)
In this article, we will explain the different aspects of measuring blood oxygen levels.
How oxygen is carried in the blood?
Blood oxygen level, or SpO2, is a measure of how much oxygen is bound to the red blood cells. The body regulates this parameter carefully to prevent tissues from necrosis. (2)
Those presenting with symptoms of respiratory distress, such as dyspnea, will need to check their blood oxygen levels.
Additionally, patients with chronic conditions need to use a pulse oximeter on a regular basis to monitor their SpO2. Examples of these illnesses include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and asthma. (3)
During times of exacerbation, monitoring blood oxygen levels become indispensable for therapeutic assessment. It is a vital test for orienting the treatment.
How do we measure blood oxygen levels?
Arterial blood gas
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures the amount of oxygen in the bloodstream. It also detects the levels of other gases and pH. The sensitivity of this test is very high. However, it may be deferred due to its invasiveness. (4)
Using a catheter, a healthcare professional will draw blood from the patient’s artery. This will give accurate readings about the level of arterial oxygenation.
The most common location used to get these measurements is the wrist. Patients often complain of feeling uncomfortable when undergoing an ABG test.
Pulse oximeter
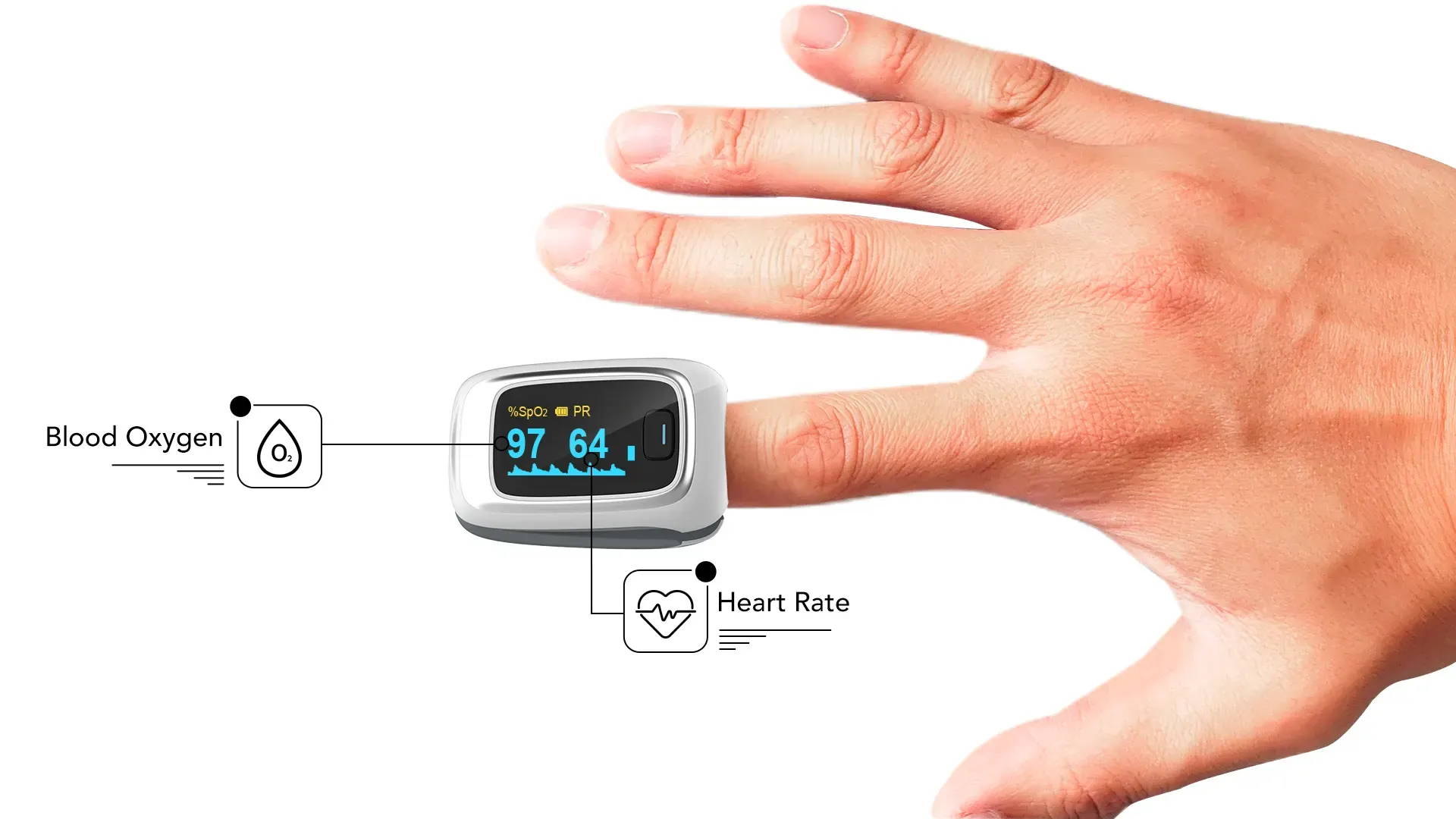
A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive tool that measures SpO2. By sending infrared signals to the capillaries of the finger, it is able to estimate how much light gets reflected off the gases.
The reading obtained from a pulse oximeter is given in a percentage. Usually, the margin error of these devices is below 2% (more on that later). (5)
Due to the ease of use of this device, it has become extremely popular among healthcare professionals. In a few seconds, doctors are able to get an estimation of blood oxygen levels without requiring an ABG test.
Today, every emergency department and doctor’s office has a pulse oximeter.
What does a normal blood oxygen level look like?
Using a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen saturation will provide the healthcare professional with a percentage. However, we still need to ask ourselves about normal blood oxygen levels.
The following guidelines will explain the different possible readings on a pulse oximeter and their respective interpretation:
Normal blood oxygen level
A healthy individual with no pulmonary problems will have normal blood oxygen levels between 95% and 100%.
The American Thoracic Society emphasizes that blood oxygen levels should be above 89% to be within the normal range.
These ranges are not clear-cut. For instance, patients with COPD or other lung diseases may have a SpO2 below 95% without actually dealing with any symptoms. According to one study, patients with severe COPD may have a SpO2 between 88% and 92%. (6)
Low blood oxygen level
A blood oxygen level below 95% is considered abnormal. Hypoxemia occurs for a variety of reasons and could lead to severe complications in organs and tissues.
As we just established, patients with chronic lung diseases may not follow the same rule.
The importance of a high-quality SpO2 to get accurate readings
The accuracy of a pulse oximeter is extremely important. The readings obtained from this device will decide therapeutic approaches and therefore, the prognoses of patients. Using a high-quality pulse oximeter to measure SpO2 is indispensable for optimal patient care.
According to the American Food and Drug Administration (FDA), companies that produce prescription oximeters must provide results with an accuracy rate that does not shift beyond 6%.
Takeaway message
Understanding normal blood oxygen levels is very important to improve patient care and prevent occult hypoxemia. What’s equally important, however, is having access to a high-quality pulse oximeter that takes accurate measures.
We hope that this article managed to highlight the different aspects of using a pulse oximeter and how it helps with orienting the management plan.
If you have any questions, concerns, or personal stories that you want to share, feel free to do so in the comment section below. For those seeking a private conversation, reach out to us via this link.
References
1-Torp, K. D., Modi, P., & Simon, L. V. (2021). Pulse oximetry. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
2-Rhodes, C. E., & Varacallo, M. (2019). Physiology, oxygen transport.
3-Buekers, J., Theunis, J., De Boever, P., Vaes, A. W., Koopman, M., Janssen, E. V., Wouters, E. F., Spruit, M. A., & Aerts, J. M. (2019). Wearable Finger Pulse Oximetry for Continuous Oxygen Saturation Measurements During Daily Home Routines of Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Over One Week: Observational Study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 7(6), e12866. https://doi.org/10.2196/12866
4-Castro, D., Patil, S. M., & Keenaghan, M. (2021). Arterial Blood Gas. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
5-Poorzargar, K., Pham, C., Ariaratnam, J., Lee, K., Parotto, M., Englesakis, M., Chung, F., & Nagappa, M. (2022). Accuracy of pulse oximeters in measuring oxygen saturation in patients with poor peripheral perfusion: a systematic review. Journal of clinical monitoring and computing, 10.1007/s10877-021-00797-8. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-021-00797-8
6-Abdo, W. F., & Heunks, L. M. (2012). Oxygen-induced hypercapnia in COPD: myths and facts. Critical care (London, England), 16(5), 323. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11475
WRITTEN BY VIBEAT
Related Blogs
Recommended Products





